Cloud Services: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Introduction
Cloud computing transformed IT operations through its delivery of flexible scalable solutions to businesses. The “Cloud services IaaS PaaS SaaS” framework acts as key infrastructure because it manages the full spectrum of infrastructure, platforms and software systems. Different businesses leverage Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) because these models provide distinctive advantages for each use. The following text delves into these three cloud service models whereby their features along with benefits and applications and transformation potential for business operations will be examined in detail.
3 Main Categories of Cloud Services
The three main types of cloud services operate under the models known as IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. These cloud service models enable businesses to select the perfect option which best suits their requirements through distinctive control schemes and flexibility and management features.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Through IaaS companies obtain remote server capabilities as well as storage capabilities and networking capabilities from the cloud. Businesses that leverage cloud infrastructure solutions from AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud acquire IaaS capabilities to increase their computing capacity without buying hardware appliances.
Key Features of IaaS:
The user can obtain computing resources on an as-needed basis through infrastructure rentals.
A business can adjust their computing power levels by expanding or contracting operational capacity easily.
Users must pay only for the specific services they utilize under this payment system.
Benefits of IaaS:
Your infrastructure should be adjustable to achieve business requirements.
The expense for physical hardware becomes unnecessary due to IaaS.
Multiple location infrastructure deployment in IaaS systems ensures high system availability to customers.
IaaS Use Cases:
For disaster recovery purposes IaaS provides rapid solutions to restore operations during failure situations.
Startups avoid spending money on hardware along with data center facilities before their business takes off.

PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS delivers a production-ready platform which serves developers to build applications in addition to application management and runtime capabilities. Within this service model developers can write code and create software because the service provider administrates both systems infrastructure and software platform requirements.
Key Features of PaaS:
A platform as a service system includes development tools that provide testing features while supporting application creation and project deployment functions.
The cloud service provider operates under full responsibility for managing all platform infrastructure.
The platform enables organizations to develop proprietary applications at their business without handling the implementation infrastructure.
Benefits of PaaS:
Development speed increases because developers can launch platform creation projects rapidly.
Staff members can efficiently collaborate on a single project through a shared environment.
The cloud service provider executes automatic system updates as part of their maintenance responsibilities.
PaaS Use Cases:
The development of web applications through mobile apps works perfectly on PaaS platforms.
API developers can build integration endpoints through the API development tools available in PaaS platforms.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Through the Internet SaaS delivers complete functional applications to users. Businesses that subscribe to SaaS receive remote access to software applications but never need to install or maintain the system nor update its versions. Three widely recognized SaaS solutions in the market include Google Workspace along with Salesforce and Dropbox.
Key Features of SaaS:
Users can access the software through their web browsers without requiring any installation process.
SaaS providers conduct all maintenance activities involving security updates to the software.
Service consumers pay monthly or annual charges according to a subscription plan to access the service.
Benefits of SaaS:
SaaS applications provide users with a simple ready-made experience because they do not need complicated setup procedures.
By using SaaS application users can reduce their expenses because they no longer need to maintain on-site software and hardware.
Customers can access SaaS applications any time because they work through any internet connection.
SaaS Use Cases:
Gmail together with Microsoft Outlook represent well-known instances of SaaS email services.
The project management software Trello alongside Asana and Slack enables businesses to both work together and run their projects.
Key Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
The following table serves companies to detect fundamental distinctions between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS for making suitable business model choices.
|
Feature |
IaaS |
PaaS |
SaaS |
|
Management |
Full control over infrastructure |
Limited control, managed platform |
No management required |
|
Customizability |
High |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Cost Structure |
Pay-as-you-go |
Subscription-based |
Subscription-based |
|
Use Case |
Infrastructure needs, flexibility |
App development, software deployment |
Ready-to-use software |
|
Examples |
AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure |
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku |
Salesforce, Dropbox, Gmail |
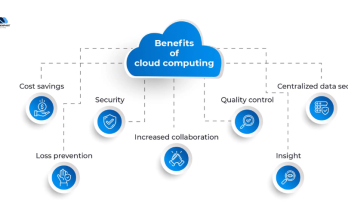
Benefits of Cloud Services: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
Businesses can select their preferred cloud model from the available choices because each approach fits particular organizational requirements. Please examine the following summary of advantages.
The three models enable businesses to reduce their expenses relating to hardware together with software.
Cloud services give organizations an automatic system to scale both their operations size and processing capabilities in response to market requirements.
Organizations maintain control freedom through cloud services since they determine the extent of infrastructure and application governance.
Cloud service providers deliver both comprehensive protective security features for data and applications to their clients.
FAQ’s
Q1 : What are the main dist inctions between the cloud service levels IaaS, PaaS and SaaS?
IaaS and SaaS differ chiefly because of control parameters. Users who need infrastructure command should opt for IaaS but PaaS serves developers of apps through managed platforms and SaaS provides complete applications with light management requirements.
Q2 : Can these three cloud service models IaaS PaaS and SaaS can operate together inside an integrated system?
Organizations adopt these services simultaneously to fulfill various business requirements. A business implements IaaS to host infrastructure yet depends on PaaS for application creation then utilizes SaaS to deal with customer relationship management.
Q3: In establishing the best model for my business which one should I select?
Your requirements will determine the best model to use. In case you require total management control of your infrastructure then IaaS should be your selection. PaaS offers the best solution when developers need to build applications while skipping infrastructure management. The choice of SaaS stands as the most suitable option when your only requirement is usage of existing software.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service
Cloud services IaaS PaaS SaaS provide businesses with various management degrees which fit their operational requirements. Every cloud service model exists to fulfill either flexibility requirements or scalability needs or user-friendly features according to your business goals. Understanding the key distinctions between IaaS PaaS SaaS will give you the knowledge to select the right service that simplifies operations and minimizes expenses. Your organization should evaluate its requirements to select the ideal cloud service model from the available options.
You May Also Like :: Understanding Cloud Computing: The Future of Technology